Colligative Properties of Solution : Molaritas, Molality and Mole Fraction
The Colligative Properties of the solution includes an explanation of molality, Molarity and mole fraction

Definition of Colligative Properties of Solution
"The colligative nature of the solution is." the nature of the solution that does not depend on the type of solute but depends on the concentration of solute particles”
The colligative nature of the solution consists of two types, namely the colligative properties of electrolyte solutions and also the colligative properties of non-electrolyte solutions
Molaritas, Molality and Mole Faction
In solution, there are several properties of substances that are determined by the number of particles of solute]. The colligative nature of the solution is determined by the number of solute particles, need to know about the concentration of the solution
Molaritas (M)
Molarity is the large number of moles of solute in 1 liter of solution.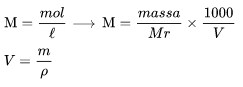
Information :
M is molarity
Mr is a molar mass of dissolved substance
V is the volume of the solution,
Molalitas (m)
Molality is the number of moles of solute on 1 kg (1000 gram) solvent.
Molality is defined by equations:![]()
Information:
m is molality (mol / kg)
Mr is a molar mass of dissolved substance (g / mol)
mass is the mass of the solute (g)
P is the mass of the solvent (g)
Mol fraction
The mole fraction is the unit of concentration of all components of the solution expressed in terms of moles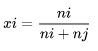
Colligative properties of Non-electrolyte solutions
Colligative properties involve solutions, Colligative properties do not depend on the interaction of solvent molecules and solutes, but depends on the amount of solute dissolved in a solution.
Colligative properties consist of :
- decrease in vapor pressure
- boiling point rise
- decreased freezing point
- osmotic pressure
Reduction in Steam Pressure
![]()
P0 = vapor pressure of pure liquid
P = vapor pressure of the solution
Increase in boiling point
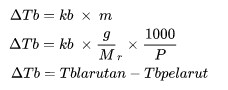
ΔTb is the boiling point increase (oC)
kb is the setting of the molal boiling point setting
m is the molality of the solution (mol / kg)
Mr is relative molecular mass
P is the amount of mass of a substance (kg)
Boiling point setting settings table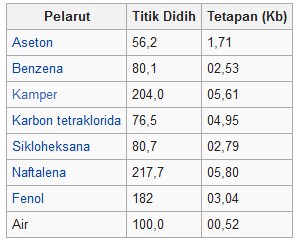
Decrease Freezing Point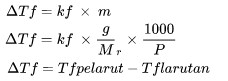
ΔTf is freezing (oC)
kf is the freeze point change setting (oC kg/mol)
m is the molality of the solution (mol / kg)
Mr is relative molecular mass
P is the amount of mass of a substance (kg
Osmotic Pressure
Π = M × R × T
Π is osmotic pressure
M is the molarity of the solution
R is the gas setting (0,082)
T is the absolute temperature
Colligative Properties of Electrolyte Solutions
At the same concentration, the colligative nature of the electrolyte solution has a greater value than the colligative nature of the non electrolyte solution. The number of solute particles resulting from the ionization reaction of the electrolyte solution was formulated by the Van & rsquo; t Hoff factor
i = 1 + (n − 1) α
Information :
i was a factor of Van's Hoff
n is the number of cation coefficients
α is the degree of ionization
Saturated Steam Pressure Reduction
ΔP = P0 × X t e r l a r u t × i
Boiling Point Increase
Δ T b = k b × m × i
Decrease Freezing Point
ΔTf = k f × m × i
Osmotic Pressure
π = M × R × T × i
Thus the discussion about the colligative nature of the solution, May be useful
Another article :
- Geometry Series Formulas and Geometry Series Problem Examples
- Virus : Structure, Classification, Shape, History and Definition and Examples of Viruses
- Magnetic field : Character, Understanding and Formulas
The post Colligative Properties of Solution : Molaritas, Molalitas dan Fraksi mol appeared first on this page.