Redox and Electrochemical Reactions : Definition and Examples of Questions
Redox and Electrochemical Reactions

Definition
Chemical reactions can be classified into various reactions. One of them is a reaction related to changes in the oxidation number of atoms before or after the reaction.
From the review of the oxidation number the reaction can be divided into 2 type ie :
The reaction group in which the atoms involved do not undergo changes in oxidation numbers before or after the reaction. Reactions in which the atoms involved do not undergo changes in oxidation numbers are called reactions that are not commonly referred to as reductions reaction not redox.
The type of reaction in which the atoms are involved in oxidation changes. Before and after the reaction the oxidation number of the atoms is not the same (change). This reaction is called an oxidation-reduction reaction (redox reaction)
Understanding Redox Reactions
Redox (oxidation reduction). Reduction is the acceptance of electrons or the reduction in oxidation numbers, while oxidation is the release of electrons or an increase in oxidation numbers
Example Reduction reaction
Cu2+(aq) + 2e ® With (s) Ag+(aq) + e ® Ag(s)
Example Oxidation Reaction
Zn(s) ® Zn2 +(aq)+ 2and Al(s) ® Al3 +(aq) + 3e
Rules for determining oxidation numbers :
- The atoms in the element have zero oxidation number
- The H atoms in the compound have an oxidation number +1
- Metal hydride (e.g. NaH, BaH2, AlH3) oxidation number H is equal to -1
- F2O compound, oxidation number O = +2
- In peroxide (H2O2, Na2O2, BaO2) oxidation number O is equal to -1
- The metal atoms in the compound have a number of positive oxidants
- The number of atomic oxidation numbers in a compound is the same as zero
- The total number of oxidation of atoms in ions is equal to the charge of ions
- If two atoms are bonded, negative oxidation numbers are always owned by atoms whose electronegativity tends to be greater
The basic concept of Redox
- Oxidation is the event of electron release or addition of oxidation numbers
- Reduction is the event of electron capture or reduction of oxidation numbers
- Reducer (reducing agent) is a substance that undergoes oxidation or substances that release electrons, or substances whose oxidation number tends to rise
- Oxidizers are substances that are reduced or substances that capture electrons / substances whose oxidation number drops
- Redox is a reaction consisting of a reduction and oxidation event or a reaction of changes in oxidation numbers
- Disproportionation reaction (autoredoks) is a redox reaction in which only one type of atom experiences a reduction and oxidation or a redox reaction in which only one type of atom whose oxidation number changes
- Electron mole is the difference between oxidation numbers
Oxidation Number Method
Steps for equalizing reactions :
- Determine the elements undergoing oxidation and reduction based on changes in the oxidation number of each element
- Equalize the number of elements that are experiencing redox by adding the appropriate coefficients
- Determine the amount of increase or decrease in oxidation numbers of elements that have changed in oxidation numbers
- Balancing changes in oxidation numbers by giving the appropriate coefficient
- Equalizes the number of H and O atoms and other elements
Half Reaction Method
Step equalization reaction:
Write down substances that experience redox reactions only
Separate the reaction into two, half reduction reaction and half oxidation reaction
Balance the redox atoms, with the exception of the hydrogen atom (H) and oxygen (THE)
Balance the oxygen atom by adding H2O molecules to the oxygen-deficient segment
Balancing a Hydrogen atom by adding H + ions to a segment that lacks an H atom
Balance the charge by adding electrons to the segment that has a more positive charge
Equate the number of electrons with the two equations of the reduction and oxidation half reactions
Putting together the two equations of a half reaction to become a complete redox reaction
Returns in the form of an initial reaction
Understanding Electrochemical Cells
Electron transfer in solution redox reactions takes place through direct contact between particles in the form of atoms , molecules or ions that pass through the electrons.
Electrochemical cell is a cell or a place where the flow of electrons caused by changes in chemical energy into electrical energy or vice versa. These cells are grouped into two types viz :
- Sel Volta
- Electrolysis Cells
Voltaic cells involve changing chemical energy into electrical energy while electrolysis cells involve changing electrical energy to chemical energy. How is the process happening?
Sel Volta
Sel Volta make use of spontaneous reactions (∆G < 0) to generate electricity, the difference in reactant energy with the product is converted into electrical energy. The reaction system does work on the environment
Sel Elektrolisa utilize electrical energy to carry out non-spontaneous reactions (∆G > 0) work environment on the system
Both types of cells use electrodes, that is, substances that conduct electricity between cells and the environment and are dipped in electrolytes (ion mixture) involved in the reaction or carrying the charge.
Voltaic Cell Components
The series of electrochemical cells was first studied by Luigi Galvani and Alessandro Volta . So it is called Galvani cell or Volta cell. Both found the formation of energy from chemical reactions. The energy produced from the chemical reaction of Voltaic cells is electrical energy
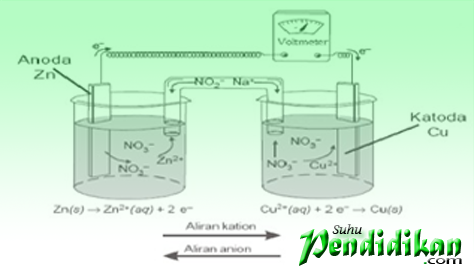
Voltaic cells consist of electrodes (zinc metal & copper) electrolyte solution (ZnSO4 and CuSO4), and salt bridges. Zinc metal and copper act as electrodes. Both are connected via a voltmeter. The electrode at which the oxidation takes place is called the anode or negative electrode, whereas the electrodes where the reduction is called the Cathode or positive electrode
Note Sel Volta
•Voltaic cells are denoted in the manner agreed upon (for Zn / Cu2 + cells)
Zn(s)|Zn2 +(aq)║Cu2+(aq)|With(s)
Examples of Redooks
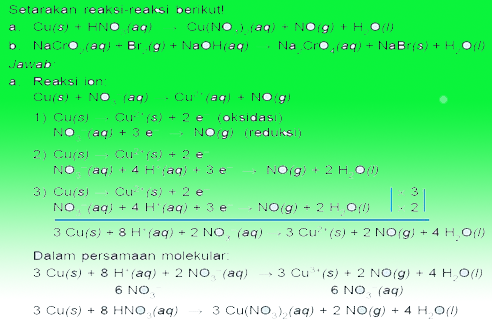
Thus the language of redox and electrochemistry, May be useful
Another article :
- Colligative Properties of Solution : Molaritas, Molality and Mole Fraction
- Geometry Series Formulas and Geometry Series Problem Examples
- Virus : Structure, Classification, Shape, History and Definition and Examples of Viruses
The post Redox and Electrochemical Reactions : Understanding and Examples of Problems appearing first on this page.