Benzene : Use of Benzena, Character, Formula, Structure, and Examples
About Benzene

What is Benzene
Benzene is commonly known as benzene, namely organic chemical compounds which are colorless and flammable liquids and have a sweet odor.
Benzene consists of 6 the carbon atoms that make up the ring, with 1 hydrogen atoms bonded to each 1 atom carbon. Benzene is a cyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with a fixed pi bond. Benzene is a component of petroleum, and is one of the basic petrochemicals and solvents which are important in the industrial world.
Because it has a high octane number, hence benzene is one of the important compounds in gasoline. Benzene is also a basic ingredient in the production of drugs, Plastic, fuel, artificial rubber, and dyes.
Benzene is a natural ingredient in petroleum, but generally obtained from other compounds in petroleum. Because it has carcinogenic properties, hence its use other than non-industrial sectors is very limited.
Benzene formula
chemical formula C6H6, PhH
Benzene derivatives
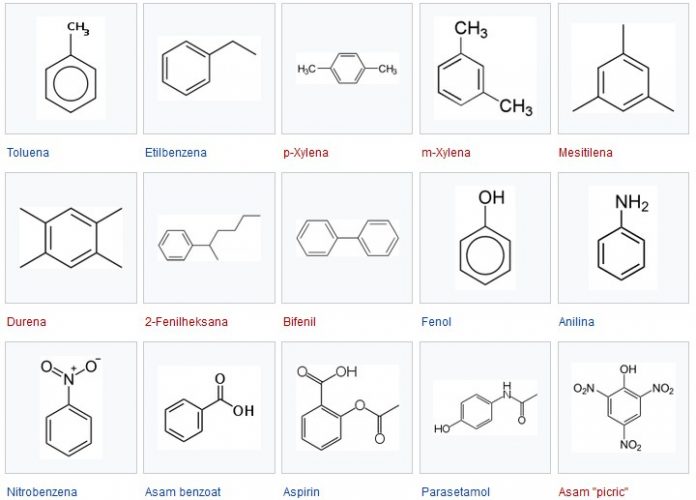
Many chemical compounds come from benzene. A compound made by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms in benzene with other functional groups.
Examples of simple benzene derivatives are :
- Phenol
- Toluene
- Aniline
The carbon atoms on the benzene ring are replaced by other elements. One of the most important derivative compounds is the nitrogen-containing ring. Substituting one CH for N can form the pyridine compound pyridine, C5H5N. Although benzene and pyridine are structurally related, However, benzene cannot be converted into pyridine.
The replacement of the second CH bond with N can form a pyridazine compound, pyrimidine or pirazine depends on the position of the N atom which replaces CH.
Benzene Uses
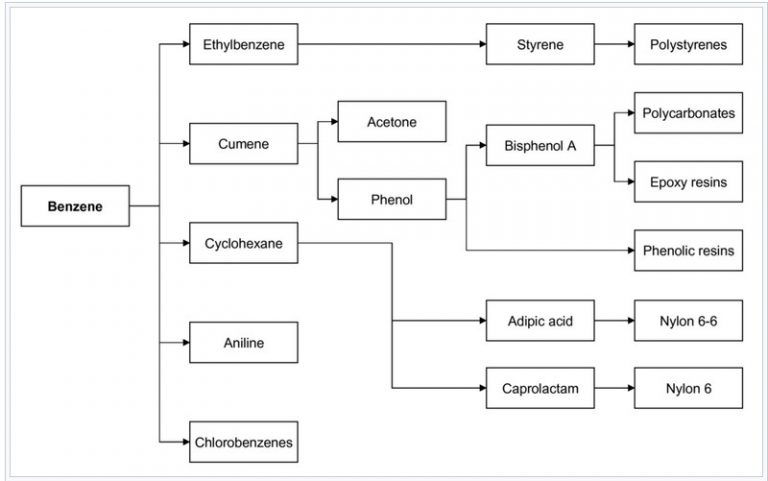
Benzene is generally used as a base for other chemical compounds. Around 80% benzene consumed inside 3 the main chemical compounds namely :
- etilbenzena
- to break
- cyclohexana
The best known derivative is ethylbenzene, because it is a raw material for styrene, which will later be produced into plastics and other polymers. Cumene is used as a raw material for resin as well as an adhesive. Cyclohexane is used in making nylon. Small amounts of other benzene are also used in the manufacture of rubber, lubricant, dye, drug, explosives, and pesticides.
In the United States and Europe, 50% of benzene is used in the production of ethylbenzene / styrene, 20% used in the production of cumene, and around 15% used for the production of cyclohexane.
Currently, Benzene production and demand in the Middle East recorded the highest increases in the world. The increase in production is expected to increase up to 3,7% and demand will increase 3,3% per year up to years 2018. Nevertheless, Asia-Pacific region will still dominate the world benzene market, with the demand of about half the global global demand
In laboratory research, currently toluene is often used as a substitute for benzene. The chemical properties of toluene with benzene are similar, but toluene is less toxic than benzene.
Benzene Structure
Benzene has the chemical formula C6H6. Comparison of the number of C and H atoms shows that benzene is highly unsaturated. At first, Experts suggest that benzene has an aliphatic structure in the presence of double or triple bonds. However, in fact benzene does not exhibit the unsaturation properties of such structures. The experimental results show benzene-like properties:
Benzene is very stable (not reactive).
Benzene does not react with Br2, with the exception of a catalyst. This is incompatible with the unsaturation properties of alkenes or alkenes which are very readily prepared by bromine.
Monosubstitusi atom halogen (X) in benzene it produces one kind of compound, namely C6H5
This shows that there is no geometrical isomera as in alkenes.
Another article :
- Alkana : Alkane-derived compounds, Character, Function Groups and Formulas
- Read More, Tahmid, Takbir, and Tahlil and its meaning and benefits
The post Benzena : Use of Benzena, Character, Formula, Structure, dan Contoh appeared first on this page.