Alkana : Alkane-derived compounds, Character, Function Groups and Formulas
Alkane-derived compounds: Nature and Function Groups.

What is it called the alkane? Alkanes are organic molecules that are classified as hydrocarbon compounds with a single bond. Hydrocarbon compounds are chemical compounds that contain the element hydrogen (H) and carbon (C), or commonly written as CxHy where x is the amount of carbon and y is the amount of hydrogen, while alkanes have the formula CnH2n + 2.
Properties of Alkanes
Alkanes have several properties, that is:
1. Is hydrocarbons saturated, where the number of H is maximal because there is no double bond between Cs
2. Reactivity with other chemical compounds are relatively small, this is also because alkanes do not have double bonds, because more and more double bonds, a chemical compound will be more reactive
3. Affinity small
4. The longer the carbon chain, the higher the boiling point, except isomer with many branches, then the more branches, the lower the boiling point
5. The longer the carbon chain, the greater the density, but still smaller than the density of water, so that when alkane and water are mixed, the alkanes will be in the upper phase
6. At standard temperature and pressure (STP = standard temperature and pressure), alkanes with C1-C4 chains are gaseous, C5-C17 has a liquid form, and the next C18 has a dense existence
7. Has no conductivity,that means it does not generate or conduct electricity
In general, alkanes are named according to the number of C atoms, in general that is:
- CH4: methane
- C2H6: etana
- C3H8: propane
- C4H10: butane
- C5H12: pentane
- C6H14: hexane
- C7H16: heptane
- C8H18: octane
- C9H20: nonana
- C10H22: dean.
following the explanation
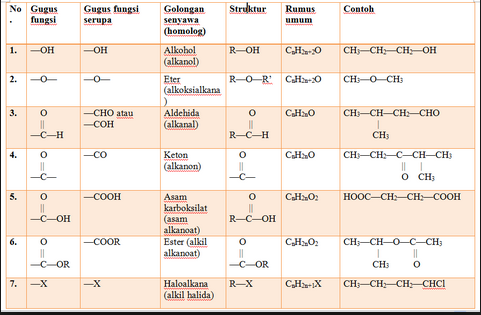
1. Alkohol/Alkanol
Functional groups: -OH
General structure: R-OH
General formula: CnH2n+2O
Example: methanol (CH3OH) and ethanol (C2H5OH) which is often used as a solvent for chemical reactions
2. Ether / Alkoxyalkana
Functional groups: -THE-
General structure: R-O-R’ (-OR’ also called an alkoxy group)
General formula: CnH2n+2O
Example: dimethyl ether (CH3-O-CH3 / C2H6O) or can be called a DME, widely used as a refrigerant.
3. Aldehid/Alkanal
Functional groups: -FOR
General structure: R-FOR
General formula: CnH2nO
Example: methane (CHOH) or often called formaldehyde / formaldehyde, which is a compound used as a preservative for corpses.
4. Keton / Alkanon
Functional groups: -C=O-
General structure: R-C=O-R’
General formula: CnH2nO
Example: propanon (C3H6O) or often called acetone which is used for nail polish remover or nail dye
5. Carboxylic Acid/Alkanic Acid
Functional groups: -COOH
General structure: R-COOH
General formula: CnH2nO2
Example: Acetic acid (CH3COOH) or often called vinegar which can be used as a food preservative, food flavor enhancers, and as one of the ingredients for making nata de coco
6. Ester / Alkyl Alkanoate
Functional groups: -COO-
General structure: R-COO-R’
General formula: CnH2nO2
Example: methyl salicylate (C8H8O3), widely used for the mixture of patches
7. Alkyl Halide / Haloalkane
Functional groups: -X
General structure: R-X
General formula: CnH2n+1X
Example: trichloromethane (CHCl3) or often called chloroform, used as an anesthetic.
Thus the discussion this time, May be useful :
Another article :
- Kinematics Material With Vector Analysis With Sample Problems
- Isomer : Definition, Structure , Formula and Isomer c7h16
- Complete Human Digestive System
- Chemical elements : Gas Mulia, Halogen, Alkail Metals, Alkaline Soil and Periodic Elements
The post Alkana : Alkane-derived compounds, Character, Gugus Fungsi dan Rumus appeared first on this page.